Infra Structure Security

Our Clint Rating: 4.8 Start Based on 24 users
Physical Access Control Solutions including Time Attendance
It’s very common today for even a small bakery shop or a grocery store to implement a physical access control and a Time attendance solution.incidentally even the simplest solution is a type of security solution. physical access control solutions include the CCTV implementation, a Time attendance implementation, across the organisation and its any other branches. Scada control system with its highest degree of automation in very sensitive alias such as oil and gas, water and electricity plans, certain manufacturing companies has entered into the IT domain with its TCP/IP enablement to get connected to the enterprise network.although it adds a huge value to the organisations infrastructure management it also adds security risks and inherits the risks of Fern interconnected world where that is the PAP.because of its very sensitive nature and with the ever-growing threats and vulnerabilities present in the networking world cadre is increasingly seen as a critical asset to be on the top priority lists of many CEOs, CIOs, CTOs and the information analysts.
 Nbiz has access to very senior resources who had carried out many Scada audits, Scada implementations. Nbiz with its unique proposition of the scandalous also is and the IT resources would help organisations to identify the major risk areas as follows the scada is concerned and this can help its customers in order to provide a detailed scada analysis for a new implementation or access the current security posture in relation to the scada systems. All the bold channels of communications increasingly trigger many events or transactions are different places under different times and types at all levels in the communication ecosystem.and it is very important to capture these events among these events analyse these events: ladies events and prepare a meaningful report for the ISMS in order to bring new or improvements or redesigned the process or investigate certain security incidents.
Nbiz has access to very senior resources who had carried out many Scada audits, Scada implementations. Nbiz with its unique proposition of the scandalous also is and the IT resources would help organisations to identify the major risk areas as follows the scada is concerned and this can help its customers in order to provide a detailed scada analysis for a new implementation or access the current security posture in relation to the scada systems. All the bold channels of communications increasingly trigger many events or transactions are different places under different times and types at all levels in the communication ecosystem.and it is very important to capture these events among these events analyse these events: ladies events and prepare a meaningful report for the ISMS in order to bring new or improvements or redesigned the process or investigate certain security incidents.
The business owner can grant access to sensitive data. With the restricted access functionality, you can define access policies for your organization.
- Perimeter firewall
- Core switches, edge switches
- Routers
- Systems - Microsoft active directory, exchange, proxy, CRM et cetera, Linux-based systems or UNIX-based systems
- Legacy applications
- ERP applications (Oracle a dash business Suite, slab)
- Appliances
- Databases
- Anti-spyware, Antivirus
- Security events from different security systems (IDS, IPS,) and so on
Hence the even log management becomes an indispensable aspect for any organisation which uses information technology to order made the business processes and the supporting processes as as well. Nbiz helps its customers to place the right product in the events management domain.
It is being practiced on different organizations. One of the reason being considered during the enhancement on the proper security analysis aspects, it requires a special skill sets for the competencies and review the security controls .
To assist you, Nbiz provides you the best soulution for physical security solutions according to your organization evnvironment.Below are the few products where we nbiz provides the best security solutions once you engage our services.
- Access control systems-For More Details Click here
- CCTV Systems
- Door Access systems
- Biometric Access systems
- Time attendance System web applications
Introduction
To insure that the ever-changing security requirements of a facility are met, a periodic review of a site’s access control system and its associated policies is a necessity. In fact, conducting an annual access control system review is the first step in establishing a systematic process for assessing the security of your organization; it is the principle best practice that provides the framework for all the other guidelines.
Once a yearly review process is in place, the fundamental best practices concept is that an effective security system uses a layered approach to security. A good analogy of this concept would be one where a home protected by a burglar alarm might use both glass break detectors and motion sensors to detect when an intruder enters the house.Choosing the Right Reader and Card Technology Contactless smart cards are fast becoming the technology of choice for access control applications. Security, convenience, and interoperability are the three major reasons for this growth. Since there are a wide variety of reader technologies being offered by today’s manufacturers, it is important to make sure that the correct technology is chosen to match the desired level of security. Using a good, better, best grading system will help make the correct choice easier.
Recognizing that there are many legacy card technologies still in use and that replacing them with the latest contactless smart card technology may be expensive or logistically difficult, implementing the recommendations included in this paper will raise the level of security of an installation and should be done regardless of the card technology employed
Relative Security of Commonly Used Card Technologies Figure 1 illustrates and ranks the relative strength of commonly used card technologies based on how much publicly available information there is about the technical details of the card technology and the degree of difficulty required to illegally read or copy from the technology. The higher the number, the more secure the technology:
Figure
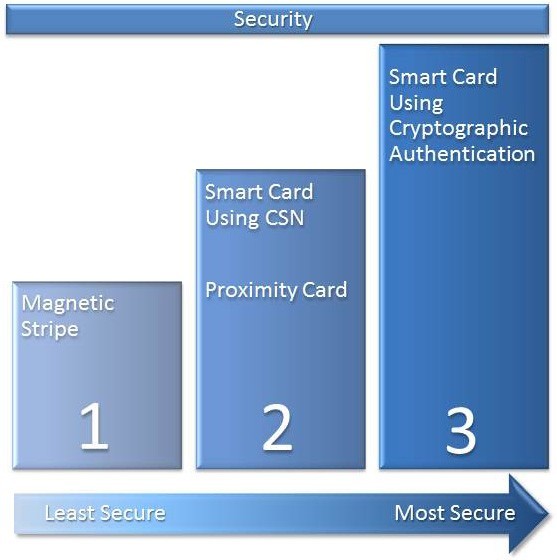
Relative Security Levels of Commonly Used Card Technologies (lowest to highest)
Magnetic stripe (magstripe) has the lowest security with its technical details being well documented by ISO standards. This technology typically uses little or no security protections. Additionally, offthe-shelf devices are widely available to encode magstripe cards. Although there are some techniques that can make magstripe more secure, widespread adoption of these techniques in the access control industry have not occurred due to the convenience, security, and increased memory available in contactless smart cards. 125 kHz proximity (Prox) card technology and the use of the Card Serial Number (CSN) of a contactless smart card are better than magnetic stripe but are not as secure as contactless smart cards. Prox card devices that can copy and emulate (mimic) Prox cards have been demonstrated. Similarly, because there is no secure authentication of the CSN and the knowledge of the CSN workings are published as part of the ISO standards, CSN emulation is also easily accomplished. (For more details on the dangers of using CSN readers, see the Appendix that describes these dangers in greater detail.)
Contactless smart cards, when properly implemented and deployed, offer the highest level of security and interoperability. These cards use mutual authentication and employ cryptographic protection mechanisms with secret keys. They may also employ special construction and electrical methods to protect against external attacks. Use Proper Key Management Key management deals with the secure generation, distribution, storage, and lifecycle management of cryptographic keys. This important subject deserves an entire white paper by itself, but here are a few of the essential key management best practices.
Whenever there is a choice, choose a manufacturer that allows you to utilize your own cryptographic authentication key that is different that its other customers so you have a unique key for your facility or organization. Although it may be easier not to have the responsibility of managing and safeguarding your own keys, utilizing your own authentication keys will protect your organization from a key compromise that occurs in someone else’s readers purchased from the same manufacturer.
Do not choose a manufacturer that stores the same key in all of its credentials. Extraction of the key from a single card compromises all of the cards in use. Use a manufacturer that uses diversified keys, which means that each card uses a different key that is cryptographically derived from a master key. Ideally this diversification would use a public scrutinized algorithm such as DES or AES.
Use Security Screws
Always utilize security screws that require special tools to remove a reader and other security components. If the correct tool is not available, then it makes it nearly impossible to remove the reader without causing damage to the screws. This damage may be noticed alerting security of a potential intrusion attempt – especially if policy dictates that readers be physically examined on a periodic basis. (Physical examination of readers should be included on guard tours.) It also has the effect of making the removal process more difficult, and slowing down the removal increases the possibility that the perpetrator will be noticed. Prevention Using Antipassback Another best practice that may be feasible is to program the access control host software to refuse granting access to a cardholder that is already inside the facility, which will prevent a duplicate card from entering the facility. This mechanism, referred to as antipassback, is available in many access control systems. Note that this feature requires two readers at the door – an ‘in’ reader and an ‘out’ reader. One additional benefit of using antipassback is that it prevents a user from using their card with others following through an open door (tailgating). Use Additional Factors of Authentication It is generally accepted that multiple factors of authentication consisting of something you have (e.g., a card), something you know (e.g., a password), and something you are (e.g., a biometric) increases the probability that the person presenting his card at a reader is the same person that was initially issued the card. Ideally the use of all three factors is best but just adding one additional factor can be effective.
A relatively inexpensive, easy-to-use second factor is a password, which can be achieved with the use of card readers with built-in keypads. Keypad readers are ideal solutions for environments where additional layers of security are required – such as in a lab or corporate research environment and the perimeter entrances to a facility




 Special Offers
Special Offers
 GET OUR BEST DEALS!
GET OUR BEST DEALS!